PR/MR Workflow¶
Info
In this documentation all references to pull requests can be change to merge requests for GitLab. However, the resulting Kubernetes object will still be named TerraformPullRequest.
Components¶
The server¶
Info
For more information about the server, see the architectural overview documentation.
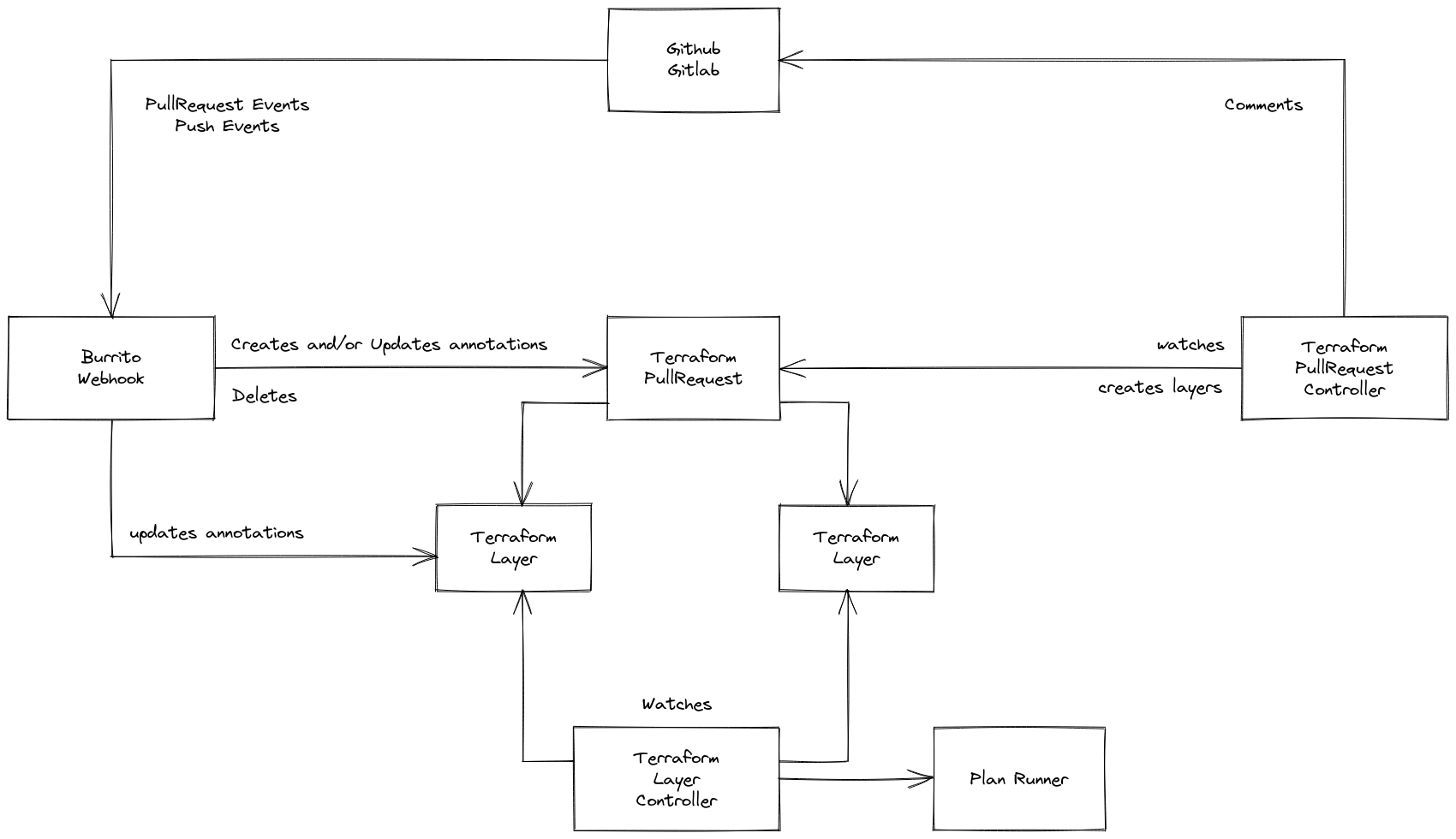
Upon receiving a Pull Request creation event, the server creates a TerraformPullRequest resource.
Upon receiving a Pull Request deletion event, the server deletes the related TerraformPullRequest resource.
The pull request controller¶
The pull request controller is a Kubernetes controller which continuously monitors declared TerraformPullRequest resources.
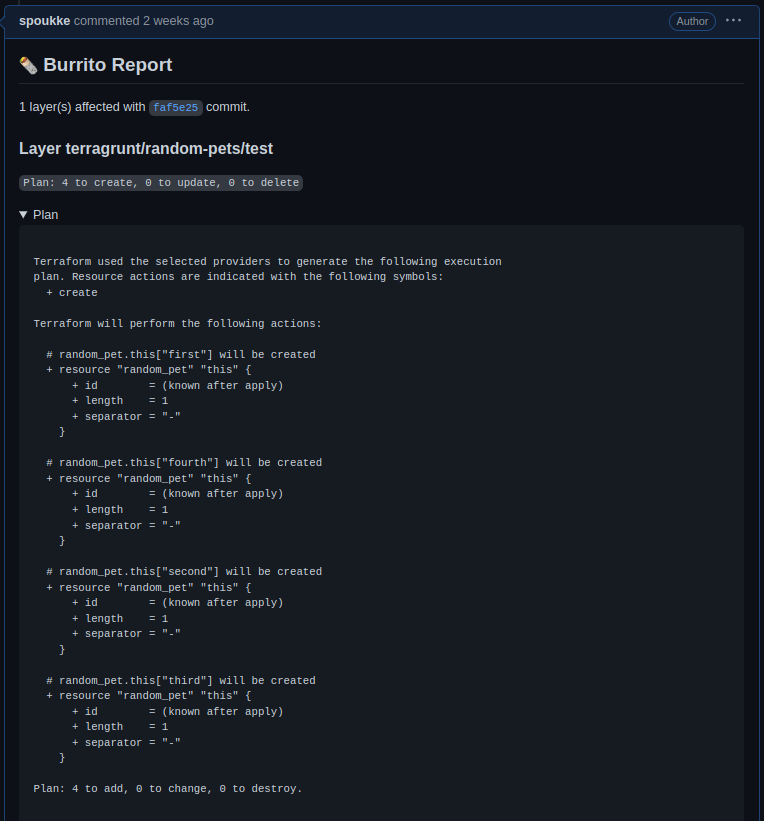
It is responsible for creating temporary TerraformLayer resources linked to the Pull Request it was generated from. Once all the TerraformLayer have planned, it will send a comment containing the plan results to the pull request.
Implementation¶
The status of a TerraformPulLRequest is defined using the conditions standards defined by the community.
3 conditions ared defined for a pull request:
IsLastCommitDiscovered. This condition is used to check if we received a new commit on the pull request by comparing the latest commit on the branch and the last discovered commit.AreLayersStillPlanning. This condition is used to check if all the temporary layers have finished planning. This is done by checking all the resultingTerraformLayerstatuses.IsCommentUpToDate. This condition is used to check if the controller needs to send a comment to a pull request. This is checked by comparing the last discovered commit and the last commit for which a comment was already sent.
Info
We use annotations to store information.
With those 3 conditions, we defined 3 states:
Idle. This is the state of a pull request if nothing needs to be done.DiscoveryNeeded. This is the state of a pull request if the controller needs to check which layers are affected on the given pull request.CommentNeeded. This is the state of a pull request if the controller needs to send a comment to the git provider's API.
Configuration¶
Webhook¶
Follow the instructions in Setting up a Git Webhook to configure a webhook in your repository. The webhook will be used to trigger:
- Drift detection when a push event is received.
- The PR/MR workflow when a pull request event is received.
Git Authentication Methods¶
For the PR/MR workflow to function properly, you need to set up authentication to your Git provider. You can use one of the following authentication methods:
- GitHub App Authentication - Recommended for GitHub repositories
- GitHub Token Authentication - Alternative method for GitHub repositories
- GitLab Token Authentication - For GitLab repositories
Each method requires you to create credentials in a Kubernetes Secret, either as repository-specific credentials or shared credentials. For more details on credential management, see the Git Authentication documentation.